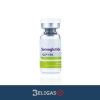
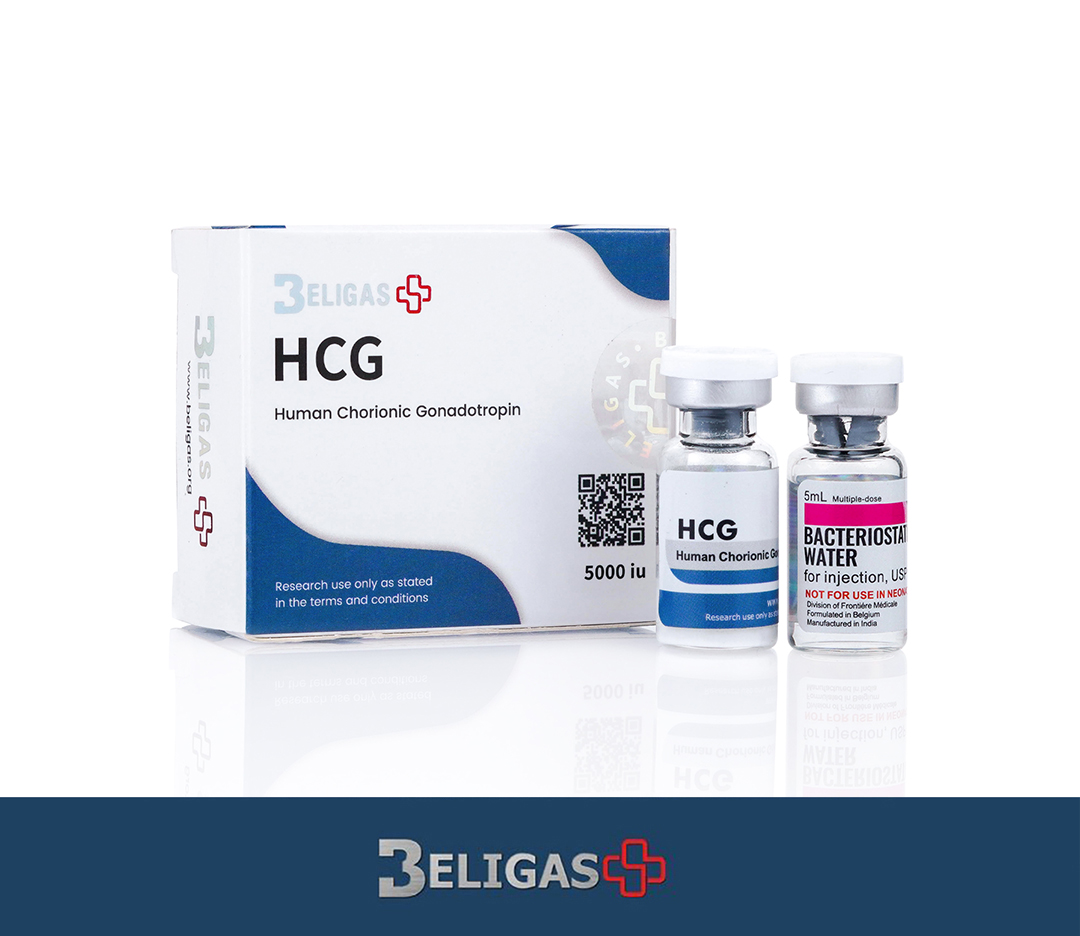
HCG 5000IU
$100.00
PROFILE
Raw:
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG)
Chemical Name:
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin: A glycoprotein hormone with two subunits, α and β. The β subunit is unique to HCG and is responsible for its biological activity.
Effective Dose (Men):
- 500 to 5000 IU per week, depending on the purpose (e.g., post-cycle therapy, HRT, or fertility treatment)
Effective Dose (Women):
- 5000 IU per week, used primarily for fertility treatments
Active Life:
- 2-3 days in the body
Detection Time:
- Up to 7-10 days, depending on dosage and testing methods
Formulation:
- Injectable Solution (5000 IU/vial, typically reconstituted with sterile water)
Out of stock
CompareKey Information about HCG 5000 IU
Primary Use:
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a glycoprotein hormone commonly used in medical treatments for both men and women. It is primarily used in fertility treatments to stimulate ovulation in women and to increase sperm production in men. Additionally, HCG has applications in post-cycle therapy (PCT) for men coming off anabolic steroid cycles.
In bodybuilding, HCG is often used as part of a PCT protocol to help restore natural testosterone production after a steroid cycle. When anabolic steroids suppress natural testosterone, HCG stimulates the testes to produce testosterone by mimicking Luteinizing Hormone (LH), which signals the testes to begin producing testosterone.
Mechanism of Action:
HCG works by mimicking the action of Luteinizing Hormone (LH), a hormone naturally produced by the pituitary gland. LH plays a critical role in the body’s ability to produce testosterone and sperm. By increasing LH levels, HCG activates the Leydig cells in the testes, which stimulates testosterone production.
For women undergoing fertility treatment, HCG is used to trigger ovulation by mimicking the luteinizing hormone surge that normally occurs at mid-cycle to release an egg from the ovary.
In men who have low testosterone or those coming off steroid cycles, HCG is commonly used in post-cycle therapy (PCT) to stimulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, which restores natural testosterone production.
Common Uses:
- Post Cycle Therapy (PCT):
HCG 5000 IU is often used after an anabolic steroid cycle to stimulate the testes and restore natural testosterone production. During steroid use, the body’s own testosterone production is suppressed. HCG helps prevent testicular atrophy and reduces the time needed for recovery. - Fertility Treatment:
In women, HCG is used to trigger ovulation in assisted reproductive treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF). It helps release mature eggs from the ovaries and encourages sperm fertilization. - Hypogonadism Treatment (Men):
In men with low testosterone (hypogonadism), HCG is sometimes used as part of a treatment regimen to stimulate testosterone production and improve fertility, especially when other methods like testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) are not viable or desirable. - Bodybuilding and Performance Enhancement:
HCG is used in bodybuilding to maintain testicular size and function during steroid cycles, especially when using compounds that suppress natural testosterone production. It is typically used in combination with other medications like Clomid or Nolvadex during PCT.
Dosing Guidelines:
Men (for PCT or Testosterone Recovery):
- 500 to 1000 IU every 2-3 days for 2-3 weeks after completing an anabolic steroid cycle. This dosage helps stimulate the testes to produce testosterone and reduces the likelihood of testicular atrophy.
- 5000 IU in a single injection: For more aggressive testosterone recovery, some individuals will inject a single large dose of 5000 IU following the completion of a cycle. This method is less commonly used and should be monitored carefully to avoid overstimulation of the testes.
Women (for Ovulation Induction):
- 5000 to 10000 IU is typically administered as a single dose to induce ovulation, typically following other hormone treatments that stimulate the ovaries (such as FSH or clomiphene citrate).
General Instructions:
- Reconstitution:
HCG 5000 IU comes in a lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder form. It must be reconstituted with sterile water (usually 1-2ml) before being injected. Ensure that the vial is mixed gently to avoid foam formation. - Administration:
HCG is typically injected subcutaneously (under the skin), either in the abdominal area or thigh. It can also be administered intramuscularly (IM), although subcutaneous administration is more common due to ease and comfort.
Side Effects:
Common Side Effects:
- Water Retention:
HCG can cause mild water retention in some users, which can result in slight bloating or swelling. - Gynecomastia (Male Breast Enlargement):
Prolonged use or high doses of HCG may lead to the conversion of excess estrogen, potentially causing gynecomastia. This is why some users combine HCG with aromatase inhibitors (AIs) to block estrogen conversion during treatment. - Testicular Pain or Swelling:
In some cases, users may experience discomfort or swelling in the testicles due to increased testosterone production. - Mood Swings:
Increased testosterone production can sometimes lead to mood swings or irritability, though this is more common when HCG is used in conjunction with anabolic steroids.
Serious Side Effects (Rare):
- Overstimulation of the Ovaries (for Women):
In rare cases, women undergoing fertility treatment with HCG can experience ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), a condition in which the ovaries become swollen and painful. This is more likely to occur with higher doses of HCG. - Blood Clot Risk (for Men):
Excessive testosterone production may increase the risk of blood clots, especially when combined with other anabolic substances or during extended periods of use.
Cycle Length:
- Post Cycle Therapy (PCT):
HCG 5000 IU is typically used for 2-3 weeks at the end of a steroid cycle, before transitioning to other PCT drugs like Clomid or Nolvadex. - Fertility Treatment:
In fertility treatments, HCG is typically administered for a short duration of 1-2 weeks, just prior to ovulation.
Stacking Options:
- With Clomid or Nolvadex (for PCT):
For optimal recovery after an anabolic steroid cycle, HCG is often stacked with Clomid or Nolvadex, which help prevent estrogenic side effects and stimulate the body’s own production of Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Testosterone. - With FSH (for Fertility Treatments):
In women, HCG is often stacked with FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) or clomiphene citrate to induce ovulation and improve fertility chances.
Related products
Beligas
Ultima
Mix Steroids