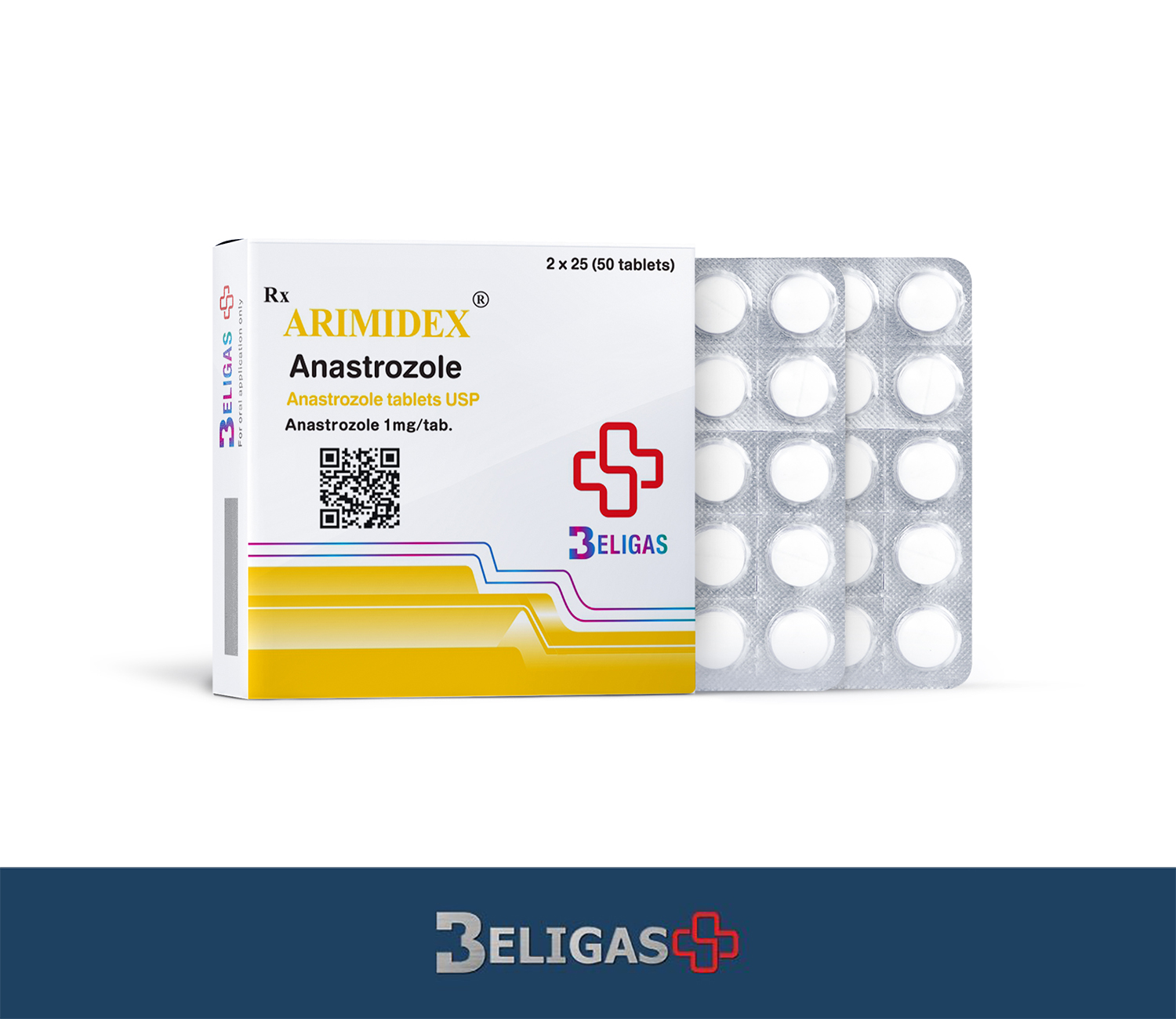
Arimidex 1mg
$130.00 Original price was: $130.00.$99.00Current price is: $99.00.
PROFILE
- Raw: Anastrozole (Arimidex 1mg)
- Chemical Name: 2,2′-(1H-1,2,4-Triazole-1,4-diyl)bis(benzenemethanol)
- Effective Dose (men): 0.5mg to 1mg per day (depending on cycle and individual needs)
- Effective Dose (women): 1mg per day (for breast cancer treatment)
- Active Life: 48-72 hours
- Detection Time: Up to 2 months (depending on testing methods)
- Anabolic/Androgenic Ratio: Not applicable (Arimidex is an aromatase inhibitor, not an anabolic steroid)
- Formulation: Oral tablets (1mg per tablet, 50 tablets per pack)
Categories: Arimidex, Beligas, PCT & Support
Key Information about Arimidex 1mg (Anastrozole):
- Primary Use:
Arimidex (Anastrozole) is a third-generation aromatase inhibitor (AI) primarily used to treat hormone receptor-positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. It is also widely used in the bodybuilding and anabolic steroid communities to manage estrogenic side effects that can arise from the use of aromatizable steroids. Arimidex works by inhibiting the aromatase enzyme, which is responsible for converting androgens (like testosterone) into estrogens. By reducing estrogen levels, Arimidex helps to prevent estrogen-related side effects such as gynecomastia (male breast tissue growth), water retention, and fat gain. - Mechanism of Action:
Arimidex works by binding to the aromatase enzyme, preventing it from converting androgens (such as testosterone and androstenedione) into estrogen. As a result, it significantly reduces estrogen levels in the body, which is beneficial in conditions where estrogen is either overproduced (like certain types of breast cancer) or when it needs to be controlled (such as during steroid use). By lowering estrogen, Arimidex helps reduce the risk of gynecomastia, water retention, and other estrogenic side effects that may occur when using aromatizable steroids. - Common Uses:
- Steroid Cycles: Arimidex is commonly used by bodybuilders and athletes during steroid cycles that involve aromatizable steroids like Testosterone, Dianabol, Nandrolone, and Methandrostenolone. By inhibiting estrogen production, Arimidex helps reduce estrogen-related side effects, including gynecomastia, water retention, and fat gain.
- Post Cycle Therapy (PCT): Arimidex is also sometimes included in PCT protocols to manage estrogen rebound and prevent side effects such as fat gain and gynecomastia after the completion of a steroid cycle.
- Breast Cancer Treatment (Women): In women, Arimidex is prescribed for the treatment of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. By lowering estrogen levels, it helps prevent the growth of estrogen-dependent tumors and reduces the risk of cancer recurrence.
- Dosing Guidelines:
- Men (Steroid Cycles):
- For most steroid cycles, the typical dose of Arimidex is 0.5mg to 1mg per day, depending on the aromatization potential of the steroids used and individual needs. Higher doses (e.g., 1mg/day) may be needed for individuals using heavier aromatizable steroids such as Testosterone or Dianabol.
- PCT (Post-Cycle Therapy): Arimidex is occasionally used during PCT to manage estrogen rebound after anabolic steroid use. The typical dose is 0.5mg to 1mg per day for 2-4 weeks, although lower doses may be effective for some individuals.
- Women (Breast Cancer Treatment):
- In postmenopausal women, the typical dose of Arimidex is 1mg per day. This is commonly used as part of adjuvant treatment to prevent cancer recurrence after surgery or radiation therapy.
- Men (Steroid Cycles):
- Side Effects:
- Joint Pain: One of the more common side effects of Arimidex is joint pain, which can be caused by the suppression of estrogen. Estrogen is important for maintaining healthy joints and bones, so reducing its levels can lead to discomfort in the joints.
- Hot Flashes: Similar to other aromatase inhibitors, Arimidex can cause hot flashes, especially when used at higher doses or for extended periods.
- Decreased Bone Mineral Density: Long-term use of Arimidex can reduce bone mineral density, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Regular bone density monitoring may be required for long-term users.
- Fatigue and Mood Swings: Some users may experience fatigue, lethargy, or mood swings, which can be linked to the drop in estrogen levels.
- Cholesterol Imbalance: Arimidex can lower HDL (good cholesterol) and increase LDL (bad cholesterol) levels, which could increase cardiovascular risk, particularly with long-term use.
- Liver Stress: Though not hepatotoxic, Arimidex can lead to mild elevations in liver enzymes in some users, particularly when used alongside other compounds that affect liver function.
- Cycle Length:
- Steroid Cycles: Arimidex is generally used throughout the entire steroid cycle to prevent estrogenic side effects. It may also be used during PCT (post-cycle therapy) for a duration of 2-4 weeks.
- PCT (Post Cycle Therapy): If used in PCT, Arimidex is typically taken for 2-4 weeks at doses ranging from 0.5mg to 1mg per day, depending on the user’s needs.
- Breast Cancer Treatment (Women): For breast cancer treatment, Arimidex is usually taken for a longer duration (up to 5 years) as part of a comprehensive treatment regimen.
- Post Cycle Therapy (PCT):
- Arimidex is sometimes included in PCT protocols to help control estrogen rebound after the cessation of anabolic steroids. After steroid cycles, estrogen levels can rise rapidly, which may lead to side effects like water retention, fat gain, and the development of gynecomastia. Arimidex helps prevent these issues by keeping estrogen levels in check.
- Typical PCT Protocol: Arimidex is often stacked with other medications like Clomid or Nolvadex during PCT. A common protocol might include Arimidex 0.5mg-1mg per day combined with Clomid or Nolvadex for 3-4 weeks.
- Stacking:
- With Aromatizable Steroids: Arimidex is commonly stacked with Testosterone, Dianabol, Nandrolone, and other aromatizable steroids to prevent estrogen-related side effects such as gynecomastia, water retention, and fat gain.
- With Other AIs: Arimidex can be stacked with other aromatase inhibitors like Aromasin or Letrozole for more aggressive estrogen control. However, excessive estrogen suppression can lead to issues such as joint pain and bone density loss.
- With SERMs: Arimidex is sometimes combined with SERMs (Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators) like Nolvadex or Clomid during PCT to both reduce estrogenic side effects and promote the restoration of natural testosterone production.
Notes:
- Estrogen Control: Arimidex is one of the most potent aromatase inhibitors and is effective at lowering estrogen levels compared to other AIs. However, excessive suppression of estrogen can lead to side effects like joint pain, fatigue, and bone density loss, so it’s important to monitor estrogen levels during use.
- Bone Health Monitoring: Long-term use of Arimidex can result in decreased bone mineral density, which can increase the risk of osteoporosis. Regular bone density tests may be recommended for users taking Arimidex for extended periods.
- Cholesterol Monitoring: Arimidex may negatively affect cholesterol levels, lowering HDL (good cholesterol) and raising LDL (bad cholesterol). Users should monitor their lipid profiles and take preventive steps to maintain cardiovascular health.
Important Considerations:
- Consult a healthcare provider before using Arimidex 1mg for PCT or breast cancer treatment, especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions like liver disease, cardiovascular issues, or osteoporosis.
- Arimidex is generally well-tolerated, but users should be mindful of potential side effects, particularly with long-term use. Regular health monitoring, including liver function, bone density, and cholesterol levels, is recommended for those using it for extended periods.