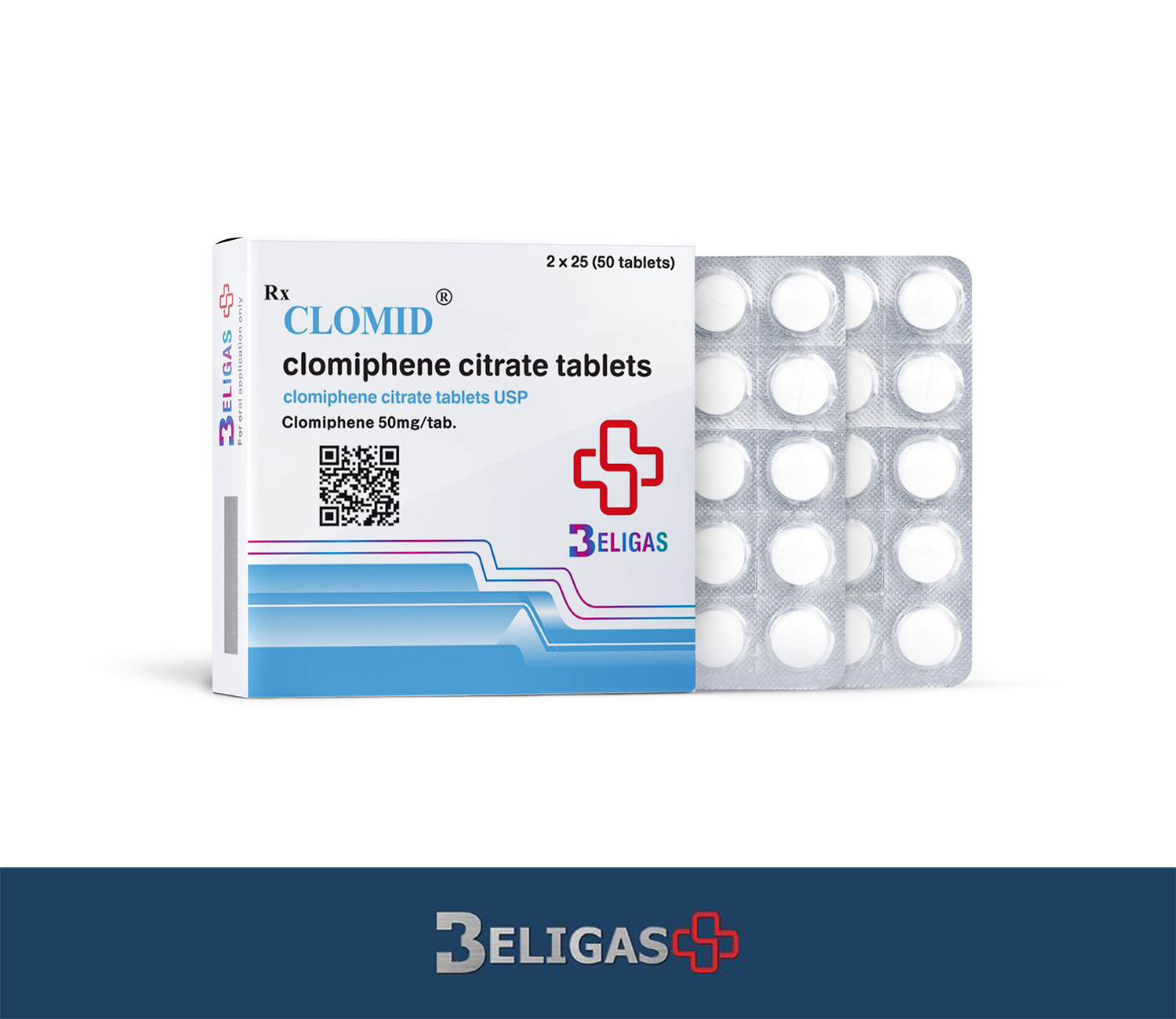
Clomid 50
$150.00
PROFILE
- Raw: Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid 50)
- Chemical Name: (±)-trans-4-[2-(P-hydroxyphenyl)-ethenyl]phenol citrate
- Effective Dose (men): 25mg to 50mg per day (depending on specific goals)
- Effective Dose (women): 50mg to 100mg per day (for fertility treatment, varies based on individual needs)
- Active Life: 5-7 days
- Detection Time: Up to 4 weeks (depending on testing methods)
- Anabolic/Androgenic Ratio: Not applicable (Clomid is a selective estrogen receptor modulator, not an anabolic steroid)
- Formulation: Oral tablets (50mg per tablet, typically sold in packs of 50 tablets)
Categories: Beligas, Clomid, PCT & Support
Key Information about Clomid 50 (Clomiphene Citrate):
- Primary Use:
Clomid 50 (Clomiphene Citrate) is a Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator (SERM) that is most commonly used for fertility treatment in women to induce ovulation. It is also used in men’s health to restore natural testosterone production after anabolic steroid cycles and during post-cycle therapy (PCT). While Clomid does not directly raise testosterone, it works by stimulating the body’s hypothalamus and pituitary gland, leading to increased secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), both of which play key roles in testosterone production in men. - Mechanism of Action:
Clomid works by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus (the part of the brain responsible for regulating hormones), which tricks the body into thinking estrogen levels are low. This causes the pituitary gland to release more gonadotropins (LH and FSH). In men, this results in increased production of testosterone by the testes. For women, it stimulates the ovaries to produce eggs and induces ovulation. Clomid has both anti-estrogenic effects (in certain tissues like the brain and pituitary) and estrogenic effects (in other tissues, such as the ovaries). - Common Uses:
- Post Cycle Therapy (PCT): In PCT, Clomid is widely used to restore natural testosterone production after a cycle of anabolic steroids. When testosterone is suppressed by steroid use, Clomid helps to “kick-start” the body’s endogenous testosterone production, improving recovery and minimizing low testosterone symptoms (such as fatigue, depression, and low libido).
- Male Hypogonadism (Low Testosterone): Clomid is sometimes prescribed to men with low testosterone levels or hypogonadism to increase natural testosterone production without the need for exogenous testosterone therapy.
- Female Fertility Treatment: In women, Clomid is primarily used to induce ovulation for those who are not ovulating regularly. It can help women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or other fertility-related issues by stimulating the ovaries to release eggs for potential fertilization.
- Dosing Guidelines:
- Men (PCT or Low Testosterone Treatment):
- Typical PCT Dose: 50mg per day for 3-4 weeks, typically starting immediately after a steroid cycle ends. The dose may be adjusted depending on individual response.
- Hypogonadism Dose: In some cases, men with low testosterone may take 25mg to 50mg per day to stimulate endogenous testosterone production and improve symptoms related to low testosterone.
- Women (Fertility Treatment):
- The typical dose for fertility induction is 50mg per day, starting on the 5th day of the menstrual cycle and continued for 5 days. If ovulation does not occur, the dose may be increased to 100mg per day or more in subsequent cycles. This is typically monitored by a healthcare provider with blood tests to assess hormone levels and follicular development.
- Men (PCT or Low Testosterone Treatment):
- Side Effects:
- Vision Disturbances: Clomid can cause visual disturbances such as blurry vision, seeing flashes of light, or visual halos, especially when taken at higher doses or for prolonged periods. These side effects are usually reversible upon discontinuation.
- Mood Swings: Users may experience mood swings, irritability, or depression, which can be exacerbated in people sensitive to hormonal fluctuations. This is especially common in women undergoing fertility treatment.
- Hot Flashes: Clomid can cause hot flashes in both men and women, as it alters estrogen levels in the body.
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): In women, Clomid can cause ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, leading to swollen, painful ovaries. This is rare but can be serious.
- Headaches and Nausea: Common side effects include headaches, dizziness, and nausea, especially at higher doses.
- Testicular Atrophy: While Clomid helps restore testosterone production in men, there is a risk that long-term use may lead to testicular atrophy (shrinkage of the testes) in some individuals.
- Gynaecomastia (Male Breast Development): Though Clomid has anti-estrogenic effects in some tissues, in others it can increase estrogen activity, which may lead to the development of gynaecomastia in men, particularly at higher doses.
- Increased Liver Enzymes: In some cases, Clomid use can lead to elevated liver enzymes, particularly if used in high doses or for long periods.
- Cycle Length:
- PCT Cycle: Clomid is typically used for 3-4 weeks following a steroid cycle to help restore natural testosterone levels. Longer cycles should be avoided due to the potential for side effects, especially with prolonged hormone manipulation.
- Fertility Treatment Cycle: In women, Clomid is generally used for 5-day cycles, with the possibility of additional cycles if ovulation is not induced during the first round.
- Post Cycle Therapy (PCT):
- Clomid is one of the most common medications used in PCT following a steroid cycle. After a cycle of anabolic steroids, testosterone production is often suppressed, and Clomid helps to stimulate the body’s natural testosterone production by increasing the levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- Clomid is typically used alongside or after other compounds like Nolvadex (tamoxifen) for an effective PCT protocol. A typical PCT regimen involves Clomid 50mg daily for 3-4 weeks.
- Stacking:
- With Nolvadex: Clomid is often used with Nolvadex (another SERM) during PCT to restore normal hormone levels and prevent estrogenic side effects. A typical combination might include Clomid 50mg/day and Nolvadex 20mg/day.
- With HCG: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) may be used before Clomid to help maintain the function of the testes during a steroid cycle and then followed by Clomid during PCT to stimulate the body’s natural production of testosterone.
Notes:
- Liver Health: Clomid is not hepatotoxic like many other anabolic steroids or oral medications. However, monitoring liver enzymes is still recommended if using other medications that can affect the liver.
- Vision Disturbances: Users should be aware of possible visual disturbances and reduce the dosage or discontinue use if they experience blurred vision or flashes of light. These symptoms typically resolve after stopping Clomid.
- Monitor Hormones: Men using Clomid for PCT should consider periodic blood tests to assess testosterone levels, estradiol, LH, and FSH levels to ensure the proper recovery of natural testosterone production.
Important Considerations:
- Consult a healthcare provider before using Clomid 50 for PCT or fertility treatment, especially if you have any pre-existing medical conditions such as liver disease, prostate issues, or a history of hormone-sensitive conditions.
- Clomid is typically used for short-term cycles to restore natural testosterone production, manage low testosterone, or induce ovulation. It is not a long-term solution for testosterone replacement or fertility treatment, and any ongoing use should be supervised by a healthcare professional.
Summary:
Clomid 50 (Clomiphene Citrate) is a SERM commonly used for fertility treatments in women and post-cycle therapy (PCT) in men to restore natural testosterone production after anabolic steroid cycles. In men, Clomid stimulates the pituitary gland to release more luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which in turn boosts natural testosterone levels. It is generally well-tolerated, though it can cause side effects such as visual disturbances, mood swings, headaches, and gynaecomastia. When used in PCT,
Related products
Sale!
Beligas
Sale!
Letrozole